“The blood pressure is the force of your blood while moving through your vessels” (American Heart Association, 2024).
Blood pressure is made up of two forces. Systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure means the blood pumped out of the heart, while diastolic pressure reflects the relaxation of your heart between beats; therefore, written as a ratio, like 120/80, and read as 120 over 80 millimeters of mercury.
HOW DO I CHECK MY BLOOD PRESSURE?
There are several ways to measure your blood pressure manually or with automated devices.
A healthcare professional should perform the manual method, as medical training is necessary to measure and interpret it accurately.
If you have your own monitor you shouldn't have a problem since they are easy to use and no medical training is necessary; however, a professional should be needed to interpret the results and make a diagnosis.
Here are recommendations to measure your blood pressure.
Before taking your blood pressure, you should:
- Avoid physical activities, smoking, and caffeinated drinks 30 minutes beforehand.
- Remove any item over the arm, including watches, bracelets, sleeves, etc.
- For the correct position: keep your back straight while sitting, do not cross your legs, and support your arm on a surface (should be flat).
- Measure at the same time every day (it’s recommended to do so before or after bed, but your healthcare provider will advise you on the best time).
- If your device has a cuff, ensure that the cuff is placed on the upper arm at heart level and that you are using the right size.
Any arm can be used for the measurement, there shouldn't be a difference.

WHAT IS THE NORMAL BLOOD PRESSURE?
A diagnosis of high or low blood pressure has to be made by a doctor or a healthcare provider.
Below, you will find the blood pressure guidelines for adults according to the American Heart Association.
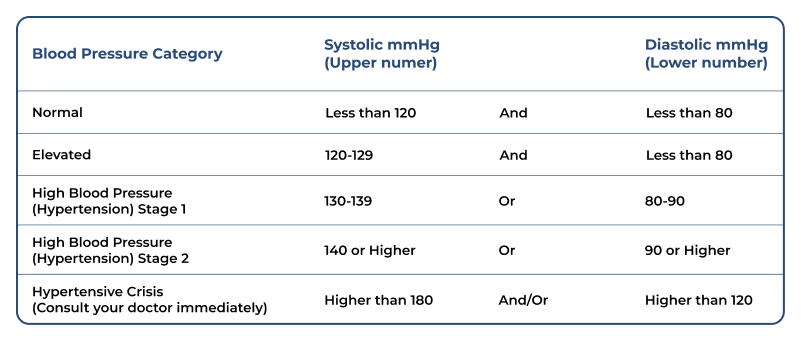
WHAT IF MY BLOOD PRESSURE IS ABNORMAL?
When blood pressure is lower than 90/60 mmHg, it’s called “hypotension”.
However, this doesn’t always indicate a problem. Low blood pressure is more common than you might think, and it usually isn't harmful if there are no additional symptoms.
Common symptoms of low blood pressure:
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Nausea with or without vomiting
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Heart Palpitations
On the other hand, when blood pressure exceeds normal levels (check the image above), it’s called Hypertension and requires constant medical monitoring. Treatment should be tailored to the individual, especially if the person has comorbidities like diabetes, obesity, or other conditions.
Unfortunately, hypertension often shows no symptoms in the early stages, which is why it is called the “silent killer”. As a result, conditions like strokes and heart attacks are common complications. Being asymptomatic does not mean your blood pressure is normal, so it is important to monitor it constantly.
Suppose high blood pressure is hereditary in your family. In that case, you can still prevent it by adopting a healthy lifestyle, reducing salt intake (including from processed foods), and avoiding smoking, among other habits.
Blood pressure can often remain normal without symptoms, but monitoring can prevent long-term damage by detecting hypertension early.
Remember, you’re not alone in this! If you’ve been diagnosed with high or low blood pressure, or if you’re just keeping an eye on it, we have tools and tips to help you stay on track. A few minutes a day can make a big difference in the long run.
Keeping an eye on your blood pressure is one of the simplest ways to take care of your heart and overall health. Even if you feel fine, high blood pressure can quietly cause serious problems like strokes and heart attacks over time.
The good news is, you can take control. By checking your blood pressure regularly, following your doctor’s advice, and making small healthy change like eating less salt, quitting smoking, and staying active you’re already doing a great job. If you notice any irregularities in one or more vital signs, contact your doctor for a professional opinion.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional advice and should not be used to diagnose any conditions. If your blood pressure is abnormal, seeking medical advice is important.
**The content on this site, regardless of its date, is not intended to replace direct medical advice from your doctor or another qualified healthcare professional**
Salyx team
References: AHA 2024 https://www.google.com/url?q=https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure&sa=D&source=docs&ust=1741905558467131&usg=AOvVaw1lIX8m4JjO8j-SKqK7t373
